If you’ve read my previous blog post you’ll know that Session-Based Desktop Deployment is now supported on Azure and can be licensed using SPLA. Details: Running VDI Session-Based Desktops on Azure now supported for SPLA
Now that this architecture is supported I thought it would be a good time to share some performance tests on Windows Azure I did earlier, to get an idea on how many concurrent sessions Azure is able to host on a single Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH) server.
For this performance test I used the following Windows Azure VM’s (all Windows Server 2012).
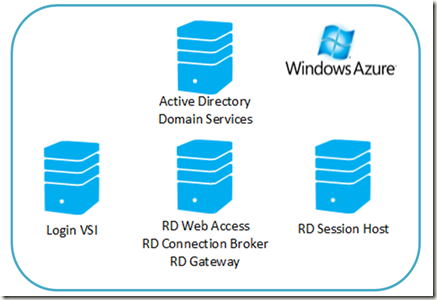
A VDI Session-Based Scenario-Based Deployment has been enrolled, and the servers are running the roles as shown below. Although technically for this test, a role-based deployment of just the RD Session Host role would have been enough because the other RDS roles are not touched within this particular load test.
To perform the load testing and benchmarking I used Login VSI. Login VSI is an industry standard benchmarking tool for measuring the performance and scalability of Virtual Desktop Infrastructures. These tests were performed before the release of 4.0 For more info also see: http://www.loginvsi.com.
Login VSI is capable of generating different types of workloads and calculates what they call a VSIMax, which is basically the maximum capacity of the RD Session Host server expressed in the amount of sessions.
The following table shows the specifications of the different Windows Azure virtual machine sizes I used for the purpose of this test.
| Azure VM Size | CPU | Memory |
| Extra Large | 8 cores | 14 Gb |
| A7 | 8 cores | 56 Gb |
I left out the VM’s with less available resources because I figured these two VM types would be most interesting since they can probably host the most number of sessions.
The following table shows the different VSI workloads (in number of sessions launched and type of workload) as well as the different Windows Azure virtual machine sizes I used for the purpose of this test. For more information on the workload types visit http://www.loginvsi.com./documentation/v3/performing-tests/workloads.
| Number | Azure VM | Workload | # Sessions launched |
| 1 | Extra Large | Medium | 30 |
| 2 | Extra Large | Medium | 40 |
| 3 | Extra Large | Light | 45 |
| 4 | Extra Large | Light | 50 |
| 5 | A7 | Medium | 40 |
| 6 | A7 | Light | 55 |
In all tests, user profiles have been pre-created for the test users and prior to each new test a reboot of the RD Session Host server has been performed to ensure everything is cleaned up properly. Also, all tests were performed several times to ensure more accuracy. Microsoft Performance monitor was also running during the tests to capture the performance counters on the RD Session Host server as shown below.
| Performance counter | color |
| Processor - % Processor time _total | Green |
| Memory – Available Mbytes | Blue |
| Terminal Services – Active Sessions | Red |
| Logical Disk – Disk Reads / Sec | Purple |
| Logical Disk – Disk Writes / Sec | Yellow |
Test number 1
| Azure VM | Workload | # Sessions launched |
| Extra Large | Medium | 30 |
![clip_image006[4] clip_image006[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjEQ6Obo7sBtcwo_BoJraLJJreUT7XHIg7SaYS2ka6k929p_MBNXUFsqRvJyCapsQ-ZIYo7-b3QB0YxVPXhgQlNFFElzAw0GOTDuAh-E9QU2kP0j6Eqfw9IDTVQfS4NLjy71D9y5rcKJoPo/?imgmax=800)
Test number 2
| Azure VM | Workload | # Sessions launched |
| Extra Large | Medium | 40 |
![clip_image008[4] clip_image008[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgERTckr6Xe5AxMsjpprrT9pkZ85JT_9-KfmhASRPOJWJENxE9-0TWsLnKQryV-JXGKURvhJdzkhYxdwmG_Pa31_dq7q0QtZTpqwSPtFFElfKN-ZmHaEowiilqcN1DsT7rEwMHv8Kble4DG/?imgmax=800)
Test number 3
| Azure VM | Workload | # Sessions launched |
| Extra Large | Light | 45 |
![clip_image010[4] clip_image010[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhQsQrg76-zHl4SZ7nDXIj8eXo7Isv2dGHLD-oMXsUzMj2SEvvSs6Quh9fwE-qs7uhLi7F1S2glRvkSSQ2AIS8ZOic9zh4niWIDWPan5slRF3Xza5hogtvZiOTIhOntEgcCYd70b7F5Pl26/?imgmax=800)
Test number 4
| Azure VM | Workload | # Sessions launched |
| Extra Large | Light | 50 |
![clip_image012[4] clip_image012[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgAnzKDSOJFyNte9Fc4UiltefHyEzTIsTQCudLQd6MRXPEctxunCX8F0TbYIlXJ2lz0O5t7vIVvIOfOny9gssOsefqLScui3X586uFtsYZMGRYbUoQFTIu02E7b-eAGoskyTHukfoDX_QYx/?imgmax=800)
Test number 5
| Azure VM | Workload | # Sessions launched |
| A7 | Medium | 40 |
![clip_image014[4] clip_image014[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj8VXYTSKs7Va_0a8KNWurESCOMfNXIcqCRYAiYIRH5AB4Z9zibDP3102LInoQFT7KbWE19dl_E4uimdVYWfTtRmGtq1dEjzx6Nh-6er6Viua3cAVePjnh3cqjwgz7X1Ew0gaFmYOYRupuI/?imgmax=800)
Test number 6
| Azure VM | Workload | # Sessions launched |
| A7 | Light | 55 |
![clip_image016[4] clip_image016[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjiX0-R2MG3Qul58tr5_izkVTTJ0jKFvpiMm_1dwLSejUV13fv-GU-2teFFCyiqTiZN50jGh59YSO_1ftd7LYWW-YWHefPMgXat37fq7plEOHdriG3vlecghN-0ivWNuK2LSifwR7OR83Lp/?imgmax=800)
Summary
As a summary, here are the results of the highest VSIMax value I got calculated per Azure VM type.
| Azure VM | Workload | VSIMax |
| Extra Large | Light | 46 |
| Extra Large | Medium | 36 |
| A7 | Light | 49 |
| A7 | Medium | 36 |
So according to the test results, these are the VSI workloads a RD Session Host (running Server 2012) is able to handle on Windows Azure. Note that these results are of course based on a Full Desktop being published. Publishing just Remote Apps obviously consume fewer resources. Also, in these tests I’ve used Office 2013 and, as you might have heard, Office 2013 causes additional resources to be used compared to previous versions of office. And I’ve used a plain Windows Server 2012 image for the RD Session Host role without any optimizations. Also note that the number of concurrent sessions (VSIMax) is a simulation, the actual performance will always vary depending on your specific applications and users. But since LoginVSi is an industry standard these workloads can be compared to other environments.
It’s interesting to see that when workloads run towards the VSIMax, available CPU is the biggest part of the bottleneck. Because CPU is the biggest part of the bottleneck, the difference in VSIMax on an Extra Large VM and A7 Azure VM (both 8 Cores) are practically the same. Since Light workloads consume less CPU and there is a difference in available memory between the Extra Large Azure and A7 Azure VM, there is a (little) difference in the VSIMax there. Therefore, environments with Light workloads could take advantage of the biggest Azure VM, the A7.
For more information on pricing and detailed specifications on Azure VM’s see:
http://www.windowsazure.com/en-us/pricing/details/virtual-machines/